Windows Compute Cluster Server 2003
(โโMicrosoft) |
|||
| ลรกdka 1: | ลรกdka 1: | ||
| โ | |||
| โ | Server | + | == Server usage == |
| โ | |||
| โ | + | The server will be kept by the Silicon Hill club. We have rich experience with servers. Calculations will be realized in cooperation with the Department of Electroenergetics of the Faculty of Electrical Engineering at CTU. In the future we will collaborate with other departments and faculties. We will also develop applications for computing clusters, such as codecs, with a support of the Department of Telecommunications Engineering. | |
| โ | |||
| โ | == | + | == Computing tasks == |
| โ | |||
| โ | |||
| โ | |||
| โ | + | '''Mathematical modeling of coupled problems of thermal and electromagnetic field in non-linear materials with hysteresis. Numerical algorithms design for there methods.''' | |
| โ | + | Mathematical modeling of simultaneous physical fields (electromagnetic, thermal, stress etc.) is one of actual tasks of present research. For so called linear materials there are | |
| โ | + | algorithms known and commercial SW available. Unfortunately ferrous alloys, very important for nearly any device, have the dependence of flux density on the intensity of magnetic field nonlinear, or, for field calculation worse, ambiguous, and the dependence is so called hysteresis curve. The research of mathematical and numerical models and algorithms is important for better understanding of the behavior of transformers, ballasts, induction-heating systems etc. These models and algorithms are studied at the Department of Electrical Power Engineering, the Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague. | |
| โ | + | The aim of the research is to study the accuracy of developed methods and their computing speed. | |
| โ | + | '''Research of effective methods of fault location using H-matrices.''' | |
| โ | + | In the case of a fault in the power grid the position of the fault has to be found as soon as possible and the error of the position assessment should be minimal. Present fault locators use relatively old algorithms and the inaccuracy of the position can be several kilometers. | |
| โ | + | Nowadays synchronous measurement of phasors is possible and so new methods of fault positioning can be used. | |
| + | The proposed use of H-matrices is in fact a problem of discrete (the position of fault) and complex continuous (impedance of the fault) optimization problem and for practical tests of developed algorithms the computation speed is an essential problem. | ||
| โ | + | '''Mathematical modeling of flooded books drying.''' | |
| โ | + | ||
| โ | Windows Compute Cluster Server 2003 | + | It is a sad fact that floods are not rare phenomena in the Czech Republic. Relatively high number of old books damaged by floods is waiting for preservation (drying, disinfection, acclimatization etc.) in deep freezers. Mr. Kyncl and Mr. Kubin from Department of Electrical Power Engineering worked on the design of multi-purpose vacuum chamber for preservation of the books. |
| + | Processes in the books while preservation consists mainly of diffusion and heat transfer. The aim is to prove developed simulation SW and determine optimal heating power and the time of the preservation process. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === The FAKE GAME project === | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Overview''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Keywords like data mining (DM) and knowledge discovery (KD) appear in several thousands of articles in recent time. Such popularity is driven mainly by demand of private companies. They need to analyze their data effectively to get some new useful knowledge that can be capitalized. This process is called knowledge discovery and data mining is a crucial part of it. Although several methods and algorithms for data mining have been developed, there are still a lot of gaps to fill. The problem is that real world data are so diverse that no universal algorithm has been developed to mine all data effectively. Also stages of the knowledge discovery process need the full time assistance of an expert on data preprocessing, data mining and the knowledge extraction. | ||
| + | |||
| + | These problems can be solved by a KD environment capable of automatical data preprocessing, generating regressive, predictive models and classifiers, automatical identification of interesting relationships in data (even in complex and high-dimensional ones) and presenting discovered knowledge in a comprehensible form. In order to develop such environment, this thesis focuses on the research of methods in the areas of data preprocessing, data mining and information visualization. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Group of Adaptive Models Evolution (GAME) is data mining engine able to adapt itself and perform optimally on big (but still limited) group of realworld data sets. The Fully Automated Knowledge Extraction using GAME (FAKE GAME) framework is proposed to automate the KD process and to eliminate the need for the assistance of data mining expert. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The GAME engine is the only GMDH type algorithm capable of solving very complex problems (as demonstrated on the Spiral data benchmarking problem). It can handle irrelevant inputs, short and noisy data samples. It uses an evolutionary algorithm to find optimal topology of models. Ensemble techniques are employed to estimate quality and credibility of GAME models. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Within the FAKE framework we designed and implemented several modules for data preprocessing, knowledge extraction and for visual knowledge discovery. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Goals''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | We are developing the open source software FAKE GAME. This software should be able to automatically preprocess various data, to generate regressive, predictive models and classifiers (by means of GAME engine), to automatically identify interesting relationships in data (even in high-dimensional ones) and to present discovered knowledge in a comprehensible form. The software should fill gaps which are not covered by existing open source data mining environments WEKA and YALE. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Experiments on the cluster''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | We currently lack computational resources for experiments with various optimization methods applied to adjust parameters of GAME units. These methods, particularly nature inspired methods such as Continuous Ant Colony Optimization, Particle Swarm Optimization, etc. are very demanding and several days are needed to finish problems of medium complexity on standard computers. With cluster of 32 cores we can run our processes in several configurations and the best configuration option can be recognized in fraction of time required at present. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We also plan to design novel methods of parallelization. Special "Niching" genetic algorithm is used in GAME and should be parallelized. We will also explore capability to maintain diversity in populations distributed over the cluster. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The cluster can be utilized also for evolution of neural networks (NEAT approach) and for computational experiments within the course Neural Networks and Neurocomputers at Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague | ||
| + | |||
| + | For more information about FAKE GAME project you can look into Mr. Kordik thesis. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Physics projects === | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | In cooperation with CTU, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Department of Physics, we have a unique opportunity to use the cluster in the following areas: | ||
| + | |||
| + | The most time and memory consuming calculations are molecular dynamics simulations, in which particle-particle interaction is evaluated and therefore the simulations are of N2 complexity. Such simulations are used for example in material science, biochemistry, biophysics, meteorology and cosmology. In physics, molecular dynamics is used to examine the dynamics of atomic-level phenomena that cannot be observed directly. Such simulations can be done only on huge computer clusters. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Another robust calculations requiring parallel computations are algorithms of the order N log N, such as tree codes or Particle in Cell methods commonly used for example in plasma physics for simulation of nonlinear wave phenomena, onset of helical and turbulent structures, magnetic reconnection processes, etc. The same | ||
| + | methods are used for simulations of sea streams, time evolution of structures of many particles such dust storms, spiral arms in galaxies, and others. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Software == | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===gridMathematica === | ||
| + | In cooperation with the Department of Electroenergetics of CTU we will receive gridMathematica 2 software from WolframResearch. It is scientific computing software that is used by top universities all around the world. It is delivers an optimized parallel Mathematica environment for modern multiprocessor machines, clusters, grids, and supercomputers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
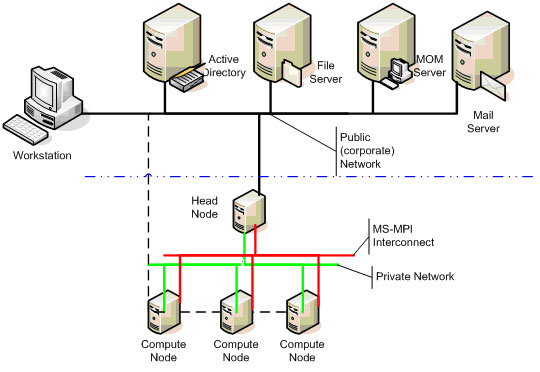
| + | ===Windows Compute Cluster Server 2003=== | ||
| + | An important partner in this project is the Microsoft Company, which will provide this project with its state-of-the-art system for computing clusters. | ||
[[Soubor:Cce overview 1.jpg]] | [[Soubor:Cce overview 1.jpg]] | ||
| + | http://www.microsoft.com/windowsserver2003/ccs/overview.mspx | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Staff == | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The solution of this project will involve: | ||
| โ | + | For CTU: | |
| โ | + | Doc. Dr. Ing. Jan Kyncl | |
| โ | + | Ing. Petr Kubรญn | |
| โ | + | Ing. Tomรกลก Novotnรฝ | |
| โ | + | CTU-FEE, Department of Electroenergetics (13115) | |
| โ | + | Ing. Pavel Kordรญk | |
| + | CTU-FEE, Department of Computer Science and Engineering (13136) | ||
| โ | + | prof. RNDr. Petr Kulhรกnek, CSc. | |
| โ | + | CTU-FEE, Department of Physics (13102) | |
| โ | + | ||
| โ | + | ||
| โ | + | ||
| โ | + | ||
| + | For Silicon Hill: | ||
| + | Jaromรญr Kaลกpar | ||
| + | Zbynฤk ฤech | ||
| + | Jan Fleiลกmann | ||
| โ | + | For Microsoft | |
| โ | + | Dr. Dalibor Kaฤmรกล | |
| โ | + | Ing. Jan Toman | |
| + | For HP | ||
| + | Jan Kuฤera | ||
| โ | + | For Intel | |
| โ | + | MuDr. Pavel Kubลฏ | |
Verze z 11. 10. 2006, 00:41
Obsah |
Server usage
The server will be kept by the Silicon Hill club. We have rich experience with servers. Calculations will be realized in cooperation with the Department of Electroenergetics of the Faculty of Electrical Engineering at CTU. In the future we will collaborate with other departments and faculties. We will also develop applications for computing clusters, such as codecs, with a support of the Department of Telecommunications Engineering.
Computing tasks
Mathematical modeling of coupled problems of thermal and electromagnetic field in non-linear materials with hysteresis. Numerical algorithms design for there methods.
Mathematical modeling of simultaneous physical fields (electromagnetic, thermal, stress etc.) is one of actual tasks of present research. For so called linear materials there are algorithms known and commercial SW available. Unfortunately ferrous alloys, very important for nearly any device, have the dependence of flux density on the intensity of magnetic field nonlinear, or, for field calculation worse, ambiguous, and the dependence is so called hysteresis curve. The research of mathematical and numerical models and algorithms is important for better understanding of the behavior of transformers, ballasts, induction-heating systems etc. These models and algorithms are studied at the Department of Electrical Power Engineering, the Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague. The aim of the research is to study the accuracy of developed methods and their computing speed.
Research of effective methods of fault location using H-matrices.
In the case of a fault in the power grid the position of the fault has to be found as soon as possible and the error of the position assessment should be minimal. Present fault locators use relatively old algorithms and the inaccuracy of the position can be several kilometers. Nowadays synchronous measurement of phasors is possible and so new methods of fault positioning can be used. The proposed use of H-matrices is in fact a problem of discrete (the position of fault) and complex continuous (impedance of the fault) optimization problem and for practical tests of developed algorithms the computation speed is an essential problem.
Mathematical modeling of flooded books drying.
It is a sad fact that floods are not rare phenomena in the Czech Republic. Relatively high number of old books damaged by floods is waiting for preservation (drying, disinfection, acclimatization etc.) in deep freezers. Mr. Kyncl and Mr. Kubin from Department of Electrical Power Engineering worked on the design of multi-purpose vacuum chamber for preservation of the books. Processes in the books while preservation consists mainly of diffusion and heat transfer. The aim is to prove developed simulation SW and determine optimal heating power and the time of the preservation process.
The FAKE GAME project
Overview
Keywords like data mining (DM) and knowledge discovery (KD) appear in several thousands of articles in recent time. Such popularity is driven mainly by demand of private companies. They need to analyze their data effectively to get some new useful knowledge that can be capitalized. This process is called knowledge discovery and data mining is a crucial part of it. Although several methods and algorithms for data mining have been developed, there are still a lot of gaps to fill. The problem is that real world data are so diverse that no universal algorithm has been developed to mine all data effectively. Also stages of the knowledge discovery process need the full time assistance of an expert on data preprocessing, data mining and the knowledge extraction.
These problems can be solved by a KD environment capable of automatical data preprocessing, generating regressive, predictive models and classifiers, automatical identification of interesting relationships in data (even in complex and high-dimensional ones) and presenting discovered knowledge in a comprehensible form. In order to develop such environment, this thesis focuses on the research of methods in the areas of data preprocessing, data mining and information visualization.
The Group of Adaptive Models Evolution (GAME) is data mining engine able to adapt itself and perform optimally on big (but still limited) group of realworld data sets. The Fully Automated Knowledge Extraction using GAME (FAKE GAME) framework is proposed to automate the KD process and to eliminate the need for the assistance of data mining expert.
The GAME engine is the only GMDH type algorithm capable of solving very complex problems (as demonstrated on the Spiral data benchmarking problem). It can handle irrelevant inputs, short and noisy data samples. It uses an evolutionary algorithm to find optimal topology of models. Ensemble techniques are employed to estimate quality and credibility of GAME models.
Within the FAKE framework we designed and implemented several modules for data preprocessing, knowledge extraction and for visual knowledge discovery.
Goals
We are developing the open source software FAKE GAME. This software should be able to automatically preprocess various data, to generate regressive, predictive models and classifiers (by means of GAME engine), to automatically identify interesting relationships in data (even in high-dimensional ones) and to present discovered knowledge in a comprehensible form. The software should fill gaps which are not covered by existing open source data mining environments WEKA and YALE.
Experiments on the cluster
We currently lack computational resources for experiments with various optimization methods applied to adjust parameters of GAME units. These methods, particularly nature inspired methods such as Continuous Ant Colony Optimization, Particle Swarm Optimization, etc. are very demanding and several days are needed to finish problems of medium complexity on standard computers. With cluster of 32 cores we can run our processes in several configurations and the best configuration option can be recognized in fraction of time required at present.
We also plan to design novel methods of parallelization. Special "Niching" genetic algorithm is used in GAME and should be parallelized. We will also explore capability to maintain diversity in populations distributed over the cluster.
The cluster can be utilized also for evolution of neural networks (NEAT approach) and for computational experiments within the course Neural Networks and Neurocomputers at Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague
For more information about FAKE GAME project you can look into Mr. Kordik thesis.
Physics projects
In cooperation with CTU, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Department of Physics, we have a unique opportunity to use the cluster in the following areas:
The most time and memory consuming calculations are molecular dynamics simulations, in which particle-particle interaction is evaluated and therefore the simulations are of N2 complexity. Such simulations are used for example in material science, biochemistry, biophysics, meteorology and cosmology. In physics, molecular dynamics is used to examine the dynamics of atomic-level phenomena that cannot be observed directly. Such simulations can be done only on huge computer clusters.
Another robust calculations requiring parallel computations are algorithms of the order N log N, such as tree codes or Particle in Cell methods commonly used for example in plasma physics for simulation of nonlinear wave phenomena, onset of helical and turbulent structures, magnetic reconnection processes, etc. The same methods are used for simulations of sea streams, time evolution of structures of many particles such dust storms, spiral arms in galaxies, and others.
Software
gridMathematica
In cooperation with the Department of Electroenergetics of CTU we will receive gridMathematica 2 software from WolframResearch. It is scientific computing software that is used by top universities all around the world. It is delivers an optimized parallel Mathematica environment for modern multiprocessor machines, clusters, grids, and supercomputers.
Windows Compute Cluster Server 2003
An important partner in this project is the Microsoft Company, which will provide this project with its state-of-the-art system for computing clusters.
http://www.microsoft.com/windowsserver2003/ccs/overview.mspx
Staff
The solution of this project will involve:
For CTU: Doc. Dr. Ing. Jan Kyncl Ing. Petr Kubรญn Ing. Tomรกลก Novotnรฝ CTU-FEE, Department of Electroenergetics (13115)
Ing. Pavel Kordรญk CTU-FEE, Department of Computer Science and Engineering (13136)
prof. RNDr. Petr Kulhรกnek, CSc. CTU-FEE, Department of Physics (13102)
For Silicon Hill: Jaromรญr Kaลกpar Zbynฤk ฤech Jan Fleiลกmann
For Microsoft Dr. Dalibor Kaฤmรกล Ing. Jan Toman
For HP Jan Kuฤera
For Intel MuDr. Pavel Kubลฏ